NFTs on Solana
- DEXArea
- Wiki
- Solana
- Token Basics
- Nfts On Solana
Introduction
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) on Solana represent unique digital assets that cannot be replaced by identical items. They are used for:
- Digital art and collectibles
- In-game items
- Tickets and passes
- Identity and credentials
- Real-world asset representation
This page explains how Solana NFTs work at a technical level, how different NFT types (standard, compressed, programmable) compare, how royalties and marketplaces behave, and what to watch for in terms of security and authenticity.
NFTs on Solana - Understanding Digital Asset Structure
What is an NFT on Solana?
On Solana, an NFT is essentially:
- A fungible SPL token mint with:
- Supply typically set to 1 (or a limited number for editions)
- Plus a metadata account from the Metaplex Token Metadata program
The mint address is the unique identifier of the NFT. The metadata holds the human-readable part: name, image, attributes, collection, and so on.
Where Ethereum has ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards built into the token interface, Solana NFTs are built on:
- SPL tokens (for balances and ownership)
- Separate metadata and edition accounts (for NFT behavior and display)
This layering gives Solana NFTs flexibility while still using the core token infrastructure.
Technical Architecture
Core Components
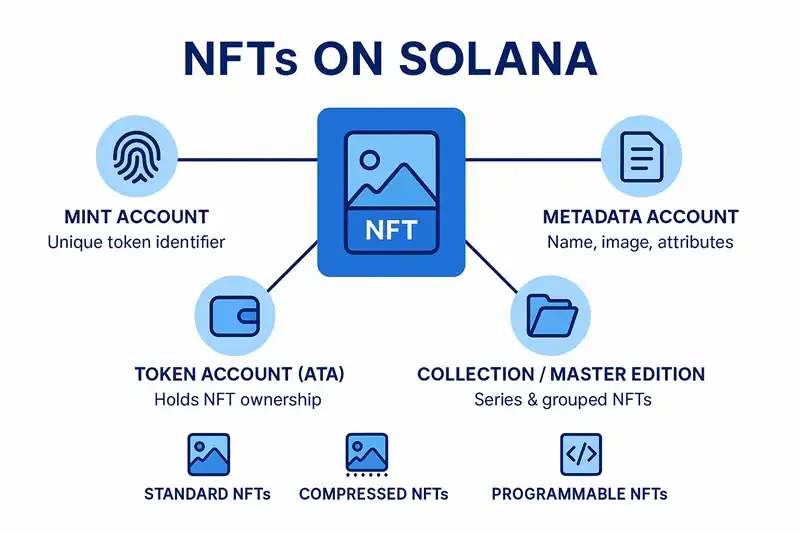
Solana NFTs consist of several accounts that together describe the asset:
Mint Account
The mint is the unique identifier of the NFT. For a typical 1/1 NFT:
- Total supply is set to 1
- Decimals are usually 0
- Mint authority is often revoked after minting
This makes the token effectively non-fungible.
Associated Token Account (ATA)
The Associated Token Account (ATA) holds the NFT for a specific owner:
- Each owner has a separate ATA for a given mint
- When the NFT is transferred, the token moves from the seller’s ATA to the buyer’s ATA
- The mint itself never changes
Metadata Account
The metadata account, managed by the Metaplex Token Metadata program, stores:
- Name and symbol
- URI (link to off-chain JSON metadata)
- Creator list and verification flags
- Collection information
- Optional attributes and properties
Wallets and marketplaces use this account to display your NFT correctly.
Master Edition & Editions
For limited series and generative drops, Metaplex uses:
- Master Edition – defines the original NFT and the maximum possible number of editions
- Edition accounts – represent each copy minted from the master edition
This is common for:
- Generative collections
- Music and media releases
- “Numbered” collectibles (e.g. #1/100, #2/100, …)
Collection
Collections are used to group NFTs and verify they belong to a specific project:
- A collection mint and collection metadata exist separately
- Individual NFTs reference the collection
- The collection relationship can be verified by the collection authority
Verified collections help marketplaces and wallets highlight legitimate project NFTs and filter out fakes.
Minting Standards & Options
Standard NFTs
Standard NFTs use:
- A mint account
- One or more token accounts
- A metadata account
- Optional edition / collection accounts
Each NFT has its own set of accounts. This model is:
- Simple and robust
- Well supported by tooling and marketplaces
- More expensive for very large collections (account rent)
Best for:
- High-value 1/1s
- Small/medium collections
- Long-term art and collectibles
Compressed NFTs (cNFTs)
Compressed NFTs (cNFTs) use Solana’s state compression and Merkle trees:
- Many NFTs are represented in a compressed Merkle tree
- Only proofs and hashes live on-chain
- Detailed data is kept in an off-chain index
Benefits:
- Dramatically lower on-chain storage and minting cost
- Practical for millions of NFTs
Common use cases:
- Large gaming inventories
- Loyalty and rewards programs
- Ticketing and event passes
Tooling and marketplace support for cNFTs is growing, but may lag behind standard NFTs in some environments.
Programmable NFTs (pNFTs)
Programmable NFTs (pNFTs) extend standard NFTs with custom transfer rules, such as:
- Royalty enforcement policies
- Compliance / allowlist checks
- Restricted transfers (e.g. only to certain addresses)
Logic is attached through the Metaplex metadata programs, rather than modifying the underlying SPL token standard.
This gives creators more control over:
- How NFTs move
- When royalties are enforced
- On-chain policy guarantees instead of pure marketplace “honor systems”
Comparison of Minting Options
| Aspect | Standard NFT | Compressed NFT (cNFT) | Programmable NFT (pNFT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage footprint | Higher (separate accounts per NFT) | Lower (compressed tree) | Higher (accounts + rule logic) |
| Minting cost | Higher per NFT | Significantly lower | Higher |
| Tooling support | Mature and broad | Growing, varies by app | Emerging but expanding |
| Transfer behavior | Standard SPL token transfers | Transfers with compression proofs | Customizable transfer rules |
| Best use cases | High-value art, smaller collections | Massive scale (gaming, loyalty, tickets) | Enforced royalties, policy-sensitive assets |
| Decentralization | High | Medium (off-chain index + proofs) | High |
Metadata & Storage
Metaplex Token Metadata Standard
The metadata JSON commonly includes:
name– NFT display namesymbol– short ticker/codedescription– human-readable descriptionimage– URI to the visual assetattributes– trait list (used for rarity and filtering)properties– more structured information, such as creators and files
The on-chain metadata account stores:
- The URI
- Verified creators
- Collection information
- Flags for mutability
Storage Solutions
Most Solana NFTs use URIs that point to:
- ✅ IPFS – content-addressed, distributed file system
- ✅ Arweave – “permanent” storage with single up-front payment
Projects often use gateways like https://ipfs.io/ipfs/... or project-specific gateways for easier browser access, while still relying on decentralized storage under the hood.
Metadata Mutability
By default, metadata can be mutable. Projects can later:
- Keep metadata mutable (for dynamic NFTs or early-stage projects)
- Make metadata immutable, preventing any changes
Immutable metadata plus verified creators and collections increases:
- Collector confidence
- Resistance to “stealth rug” metadata swaps
Royalties & Marketplace Dynamics
Royalties are intended to pay creators on secondary sales. On Solana, in practice:
- Royalties are not enforced at the base protocol level
- Enforcement depends on marketplace rules and sometimes on pNFT transfer logic
How Royalties Work in Practice
- Standard NFTs rely on marketplaces to honor royalty settings in metadata
- Some marketplaces enforce royalties by default, others made them optional
- This led to inconsistent behavior across the ecosystem
Programmable NFTs (pNFTs) aim to strengthen this by allowing:
- On-chain rules that require royalties to be paid under certain conditions
- Transfer restrictions if royalty rules are not followed
Still, users need to understand each marketplace’s policies.
Historical Context
In 2022–2023:
- Major marketplaces like Magic Eden initially enforced royalties
- New marketplaces appeared with “zero-royalty” or “optional royalty” models
- Creator income became harder to predict
This tension pushed the ecosystem towards more robust royalty tooling, including:
- pNFTs with programmable rules
- Clearer marketplace policies
- On-chain standards for showing creator preferences
For creators, it is important to:
- Publish clear royalty expectations
- Choose NFT standards and marketplaces that align with those expectations
Wallet Integration & Management
Wallet Support
Popular Solana wallets such as:
- Phantom
- Solflare
- Backpack
typically support:
- Viewing NFTs in a dedicated “Collectibles” section
- Sending NFTs to other wallets
- Connecting to marketplaces and dApps that use NFTs
Transfer Considerations
NFT transfers are:
- Irreversible once confirmed
- Final at the protocol level
Good practice:
- Double-check recipient addresses
- Use a low-value NFT to test flows with new marketplaces or wallets
- Avoid signing transactions from unknown or suspicious sites
Marketplace Integration
When listing NFTs:
- Marketplaces may use escrow accounts or escrowless models
- Fees, royalties, and listing durations vary
- Some platforms specialize in art, others in gaming or AMM-like trading of NFTs
Always review:
- Marketplace reputation and security history
- Fee structure and royalty policy
- Whether your NFT standard (standard / cNFT / pNFT) is fully supported
Costs & Performance
Solana’s low fees make NFT usage affordable, but there are still relevant costs:
- Transaction fees: Very small, but can increase with congestion or priority fees
- Account rent: New accounts (mints, token accounts, metadata accounts) require rent-exempt deposits in SOL
For large-scale NFT projects, these account costs can be significant. This is why:
- Standard NFTs are ideal for smaller, higher-value sets
- cNFTs are ideal for massive scale
For more detail on fees in general, see:
Security & Authenticity
To avoid scams and mistakes:
✅ Verify mint address
- Compare the mint address with official project sources (website, docs, X, Discord)
- Cross-check with multiple explorers if needed
✅ Check collection verification
- Many marketplaces show a “verified collection” badge
- This confirms the NFT is part of the creator-verified collection, not an imitation
✅ Watch for phishing
- Fake mints and airdrops can appear in your wallet
- Avoid connecting your wallet or signing transactions on unknown sites
- Manually type URLs or use bookmarked official links instead of random links
✅ Use hardware wallets for high value
- Store high-value NFTs in a hardware wallet
- Use a “hot” wallet only for daily interactions and minting
✅ Review approvals and connections
- Revoke old dApp permissions when you no longer use them
- Regularly clean up connected sites in your wallet
History & Evolution
Early Development (2021)
- The Solana NFT ecosystem grew rapidly with Metaplex Candy Machine becoming the standard for generative drops
- Collections like Degenerate Ape Academy helped establish Solana NFTs in the broader market
Compression Innovation (2023)
- Compressed NFTs (cNFTs) using state compression enabled:
- Millions of NFTs at a fraction of previous costs
- New use cases like large-scale loyalty and game inventories
Programmable NFTs
- Programmable NFTs (pNFTs) introduced:
- On-chain transfer rules
- Potentially stronger royalty guarantees
- Better support for regulated and compliance-sensitive use cases
Notable Programs & Standards
- Candy Machine – generative minting infrastructure for standard NFTs
- Bubblegum – compression framework for cNFTs
- Token Metadata – core metadata program for all Metaplex-compatible NFTs
Ecosystem Examples
Well-known Projects & Platforms
- Degenerate Ape Academy – early Solana blue-chip collection
- Mad Lads – popular collection and ecosystem
- Tensor – NFT marketplace with advanced trading features
- Magic Eden – early and major Solana NFT marketplace
These are examples of how different marketplaces and collections approach royalties, cNFTs, and pNFTs.
Comparison to Ethereum
Compared to Ethereum:
- Solana uses SPL tokens + metadata programs instead of ERC-721/1155
- Solana offers:
- Lower transaction fees
- Faster confirmation times
- Different trade-offs in decentralization vs performance
For users and creators who work across chains, understanding these structural differences is important when porting collections or using bridges.
Reference Tables
NFT Components & Purpose
| Component | Purpose | Control | Mutability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mint | Unique token identifier | Creator at mint time | No (core identity) | NFT’s permanent fingerprint |
| Token Account (ATA) | Holds NFT for a specific owner | Owner | Yes (balance) | Ownership changes by moving tokens |
| Metadata | Descriptive info & URI | Creator / update authority | Mutable by default, can be made immutable | Drives how NFTs display in wallets |
| Master Edition | Defines edition limits | Creator | No (once set) | Used for limited series |
| Collection | Groups related NFTs | Collection authority | Yes (assignment, verification) | Helps verify authenticity |
📝 Conclusion
Solana NFTs combine:
- SPL token mints
- Metaplex metadata and collection standards
- Optional compressed and programmable models
This gives creators a flexible toolkit for everything from 1/1 art to massive game inventories. For users, understanding:
- How NFTs are structured
- Where metadata lives
- How royalties and marketplaces actually behave
- How to verify authenticity and manage security
is critical before moving serious value into the ecosystem.
As with any on-chain asset, testing flows on devnet before committing on mainnet is strongly recommended.
❓ FAQ
Q: What’s the difference between a standard NFT and a compressed NFT?
A: Standard NFTs use separate on-chain accounts (mint, metadata, token account) for each asset, while compressed NFTs (cNFTs) use state compression and Merkle trees so only compressed proofs live on-chain. This significantly reduces storage and minting costs, especially at large scale.
Q: How do I verify an NFT’s authenticity?
A: Check the NFT’s mint address and collection against official project sources (website, docs, or social channels). Then confirm the collection is verified on reputable marketplaces or explorers before buying or interacting.
Q: Are royalties guaranteed on Solana?
A: No. Royalties on Solana are primarily creator policies, not hard protocol rules. Enforcement depends on marketplace behavior and, for some assets, on programmable NFT (pNFT) transfer rules.
Q: Where is NFT metadata stored?
A: Most NFTs store a URI in the on-chain metadata account that points to off-chain JSON hosted on IPFS or Arweave. The JSON file then points to the actual media (images, videos, etc.).
Q: What’s the difference between cNFTs and pNFTs?
A: cNFTs are about scaling and cost via compression. pNFTs are about behavior and rules, allowing custom transfer logic (like enforced royalties or compliance checks). They solve different problems and can be used in different contexts.
Q: Can NFTs on Solana be bridged to Ethereum or other chains?
A: Yes, but not natively by the Solana protocol. Third-party bridges and wrappers handle cross-chain representation. This introduces extra complexity, fees, and smart contract risk, so always research the specific bridge.
📚 References and Further Reading
- NFT with Metadata – Official Solana developer course module on NFTs
