Solana Update Authority Concepts
- DEXArea
- Wiki
- Solana
- Token Security
- Update Authority
Introduction
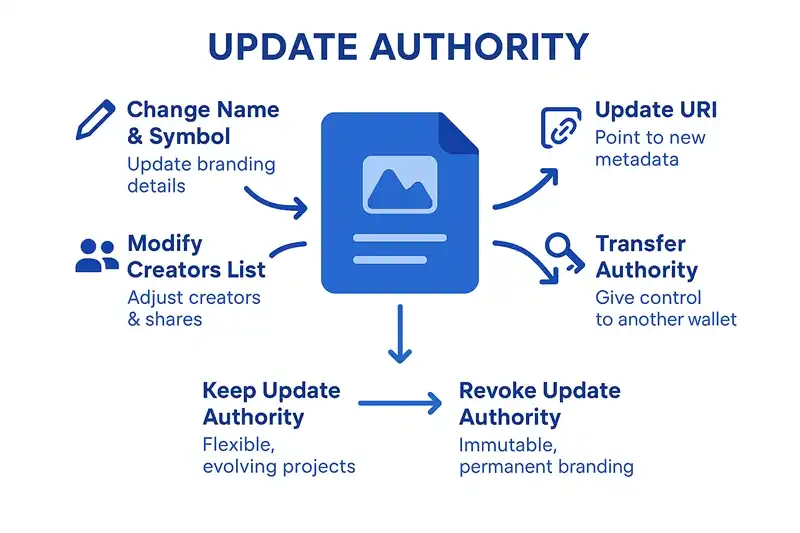
Update authority is the key that controls who can change a token’s metadata on Solana. Think of it as the “metadata controller” - only the holder of update authority can modify the token’s name, symbol, URI, and creators list.
Update Authority - Understanding Metadata Control on Solana
When you create a token on Solana, you automatically get update authority. This means you can:
- Change the token’s name and symbol
- Update the URI that points to off-chain data
- Modify the creators list and their shares
- Transfer update authority to someone else
- Revoke update authority permanently (making metadata immutable)
How Update Authority Works
Core Functionality
- Token Creation: When you create a token, you become the update authority
- Metadata Updates: You can change name, symbol, URI, and creators
- Control: You decide when and how to modify metadata
- Transfer/Revoke: You can give this power to someone else or remove it entirely
What Update Authority Controls
- Token name and symbol
- URI pointer to off-chain metadata
- Creators list and their share percentages
- Collection verification settings
- Transfer update authority to another wallet
- Revoke update authority permanently
Why Update Authority Matters
For Token Creators
- Flexibility: You can update branding and information as needed
- Trust: Users know you control the metadata
- Control: You decide the token’s public identity
For Token Holders
- Transparency: You can see who controls the metadata
- Security: You know if the token’s identity can change
- Trust: Immutable metadata builds confidence
Common Use Cases
Immutable Metadata Token
- Finalize all metadata details
- Revoke update authority permanently
- Result: Metadata is locked forever
Flexible Metadata Token
- Keep update authority active
- Update branding and information as needed
- Use for evolving projects
Multisig Control
- Transfer update authority to a multisig wallet
- Require multiple approvals for changes
- Reduces single-point failure risk
How to Verify Update Authority Status
On Solana Explorer
- Go to Solscan or Solana Explorer
- Enter your token’s mint address
- Look for “Update Authority” field in metadata
- Check if it shows an address or “None”
Real-World Examples
Community Token Implementation
Goal: Create a token with immutable brandingSteps:1. Finalize token name, symbol, and URI2. Verify all metadata is correct3. Revoke update authority4. Result: Metadata locked foreverEvolving Project Token Implementation
Goal: Create a token that can adapt over timeSteps:1. Set initial metadata2. Keep update authority active3. Update branding as project evolves4. Result: Flexible metadata for growthWhen to Revoke Update Authority
✅ Good Reasons to Revoke
- You want immutable, verifiable branding
- Your metadata is complete and final
- You want to build maximum trust
- You’re launching a “fair launch” token
⚠️ Reasons to Keep Update Authority
- You need ongoing branding updates
- You’re in early development phase
- You want flexibility for future changes
- You’re running a dynamic project
Making Metadata Immutable
What “Immutable” Means
Making metadata immutable means setting the update authority to null. This permanently prevents any changes to:
- Token name and symbol
- URI pointer
- Creators list
- Collection settings
What Immutability Doesn’t Affect
- Token supply (controlled by mint authority)
- Freeze/unfreeze ability (controlled by freeze authority)
- Off-chain content (if URI points to mutable hosting)
Risks & Mitigations
Primary Risks
Permanent Lock
- Risk: Once revoked, no metadata changes are possible
- Mitigation: Test the process on devnet first
Mutable Hosting
- Risk: HTTP URIs can still change off-chain content
- Mitigation: Use content-addressed storage (Arweave, IPFS) for URIs
Missed Fields
- Risk: Incorrect metadata cannot be corrected later
- Mitigation: Double-check all metadata before revoking
Mitigation Strategies
- Test the process on devnet first
- Use content-addressed storage (Arweave, IPFS) for URIs
- Double-check all metadata before revoking
- Have a clear communication plan
📝 Conclusion
Update authority is the key that controls metadata changes on Solana. It’s powerful but manageable and requires careful consideration of your project’s needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Keep it if you need flexibility for evolving projects
- Transfer it to multisig for shared control and security
- Revoke it when you want immutable, verifiable branding
- Always use secure key management and test on devnet first
The choice depends on your project’s needs and your security preferences. Immutable metadata builds trust and prevents manipulation, while flexible metadata enables evolution and adaptation. Consider your long-term goals and choose accordingly.
❓ FAQ
Q: What happens when I revoke update authority?
A: The metadata becomes permanently locked. No changes to name, symbol, URI, or creators are possible.
Q: Can I still change the image after making metadata immutable?
A: It depends on your URI. If it points to mutable HTTP hosting, the image can still change off-chain. Use content-addressed storage (Arweave, IPFS) to prevent this.
Q: Should I use multisig for update authority?
A: Yes, especially for team projects. It reduces single-point failure risk while maintaining flexibility.
Q: Does update authority affect token supply or freezing?
A: No. Supply is controlled by mint authority, and freezing is controlled by freeze authority. These are completely separate.
Q: Can I recover update authority after revoking it?
A: No. Revocation is permanent and irreversible. Choose carefully!
Q: What’s the difference between revoking update authority and making metadata immutable?
A: They’re the same thing! Revoking update authority makes the metadata immutable by setting the authority to null, preventing any future changes.
📚 References and Further Reading
- Solana Token Program Documentation - Official token program guide
- SPL Token Metadata Standard
- Metaplex Documentation - Comprehensive metadata and NFT tools
🔗 Related Topics
- Token Authorities - Overview of all token authorities
- Solana Token Creator Guide - How to create a new token
- How to Update Solana Token Metadata - How to modify token metadata
- Token Metadata Explained - Understanding token metadata
