How Solana Works (Simple Guide)
- DEXArea
- Wiki
- Solana
- Solana Basics
- How Solana Works
Introduction
Solana is a blockchain that works differently from others to achieve incredible speed and low costs.
This page explains how Solana works in simple terms. You’ll understand why it’s so fast, how it stays secure, and what makes it special compared to Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Here
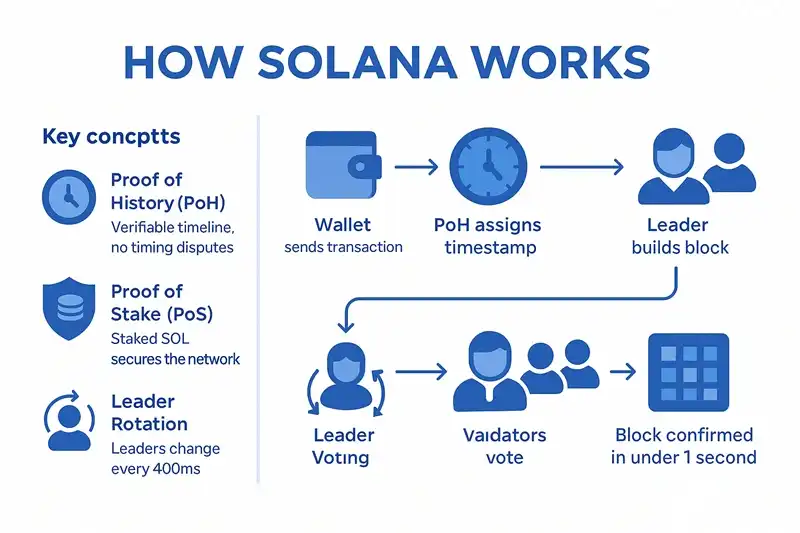
How Solana Works - Proof of History and Proof of Stake
The Big Picture: How Solana Achieves Speed
Most blockchains are slow because validators spend too much time arguing about:
- What order transactions happened in
- When each transaction occurred
- Who should create the next block
Solana solves these problems with clever innovations that make everything faster and cheaper.
Core Technologies That Make Solana Fast
Proof of History (PoH) - The Digital Clock
Think of PoH as a super-accurate digital clock that never stops.
What it does:
- Creates a verifiable timeline of all events
- Timestamps every transaction automatically
- Prevents validators from arguing about timing
How it works:
- Solana runs a continuous hashing process
- Each hash output becomes the input for the next hash
- This creates an unbreakable chain of time
- Every transaction gets stamped with this time
Why it matters:
- Validators know exactly when things happened
- No more arguing about transaction order
- Much faster block creation and validation
Proof of Stake (PoS) - The Security System
PoS is how Solana keeps the network secure without wasting energy.
What it does:
- Validators lock up SOL tokens as security deposits
- More staked SOL = higher chance to be chosen as leader
- Bad behavior results in losing staked tokens
How it works:
- Validators stake SOL to participate
- Network randomly selects leaders based on stake amount
- Leaders create blocks and earn rewards
- Other validators verify and vote on blocks
Why it matters:
- Much more energy-efficient than Bitcoin’s mining
- Faster block finality
- Better security through economic incentives
Leader Rotation - The Fair System
Solana rotates leadership fairly among all validators.
What it does:
- Different validators become leaders at different times
- Prevents any single validator from controlling the network
- Ensures decentralization
How it works:
- Leaders change every 400 milliseconds (one slot)
- Schedule is predetermined and public
- All validators know when they’ll be leader next
How a Transaction Flows Through Solana
Step 1: You Send a Transaction
- Your wallet creates a transaction
- Signs it with your private key
- Sends it to an RPC node
Step 2: Proof of History Timestamps It
- PoH gives your transaction a precise timestamp
- Places it in the correct order
- No one can dispute when it happened
Step 3: Current Leader Creates a Block
- The leader for that time slot collects transactions
- Bundles them into a block
- Includes the PoH timestamp
Step 4: Validators Vote
- Other validators check the block
- Verify all transactions are valid
- Vote to approve or reject
Step 5: Block is Finalized
- Once enough validators approve
- Block becomes permanent
- Your transaction is confirmed
Total time: Usually under 1 second!
Time Organization: Slots and Epochs
Slots - The Building Blocks of Time
- Duration: 400 milliseconds (0.4 seconds)
- Purpose: Each slot is a chance to create a block
- Leader: One validator is responsible for each slot
Epochs - The Long-Term Planning
- Duration: About 2 days (many slots)
- Purpose: Network reorganization and planning
- Activities:
- Recalculate validator stakes
- Set new leader schedules
- Adjust network parameters
Network Participants and Their Roles
Validators - The Workers
What they do:
- Process transactions
- Maintain the blockchain
- Vote on new blocks
- Earn SOL rewards
Requirements:
- Powerful computer (high-end gaming PC or better)
- Stable internet connection
- At least 1,000 SOL to stake
- Technical knowledge
RPC Nodes - The Bridge
What they do:
- Connect wallets and apps to Solana
- Submit transactions
- Provide blockchain data
- Handle user requests
Why they matter:
- Without RPC nodes, you can’t use Solana
- They’re like internet service providers for Solana
- Some are free, some charge fees
Leaders - The Block Creators
What they do:
- Create new blocks
- Include transactions
- Maintain network order
- Earn extra rewards
How they’re chosen:
- Based on amount of staked SOL
- Schedule is public and fair
- Rotates every 400 milliseconds
Why Solana is So Fast and Cheap
Speed Benefits:
- PoH eliminates timing arguments - saves seconds per block
- Efficient consensus - fewer back-and-forth messages
- Parallel processing - multiple transactions at once
- Optimized networking - data moves quickly between nodes
Cost Benefits:
- High throughput - more transactions per second = lower cost per transaction
- Efficient validation - less work per transaction
- Competition - many validators keep costs low
- No mining costs - PoS is much cheaper than PoW
Security and Reliability
How Solana Stays Secure:
- Economic incentives - validators lose money if they misbehave
- Cryptographic proofs - all transactions are mathematically verified
- Decentralization - no single point of failure
- Continuous monitoring - network watches for suspicious activity
Network Stability:
- Past challenges: Solana experienced some outages in early days
- Current status: Much more stable and reliable
- Ongoing improvements: Team constantly works on robustness
- Backup systems: Multiple layers of protection
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Sending SOL
- You send 1 SOL to a friend
- PoH timestamps it at 2:30:15.123 PM
- Leader includes it in block at 2:30:15.400 PM
- Validators vote and approve
- Friend receives SOL by 2:30:16 PM
Example 2: Trading on a DEX
- You swap SOL for USDC
- Transaction gets PoH timestamp
- Leader processes it in next block
- Validators verify the swap
- You get USDC in under 1 second
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- ✅ Extremely fast - transactions in under 1 second
- ✅ Very cheap - fees often under $0.01
- ✅ Highly scalable - 65,000+ transactions per second
- ✅ Energy efficient - no mining required
- ✅ Developer friendly - great tools and documentation
Limitations:
- ⚠️ Hardware requirements - validators need powerful computers
- ⚠️ Past stability issues - network had some outages early on
- ⚠️ Centralization concerns - fewer validators than some chains
- ⚠️ Complex technology - harder to understand than simpler chains
📝 Conclusion
Solana works by combining three key innovations:
- Proof of History - A digital clock that eliminates timing arguments
- Proof of Stake - A security system that rewards good behavior
- Efficient Consensus - A fast way for validators to agree on blocks
The result: A blockchain that’s faster, cheaper, and more scalable than most alternatives.
Why it matters: Solana makes blockchain technology practical for everyday use, from payments to gaming to DeFi applications.
❓ FAQ
Q: What happens if a leader goes offline?
A: The network automatically skips that slot and continues with the next leader. No transactions are lost.
Q: How does Solana prevent double-spending?
A: PoH ensures every transaction has a unique timestamp, and validators verify no SOL is spent twice.
Q: What if validators disagree on a block?
A: The network uses a voting system. Once 2/3 of validators agree, the block is finalized.
Q: How does Solana handle network congestion?
A: Users can add priority fees to speed up their transactions, and the network processes them in order of priority.
Q: What makes Solana different from other fast blockchains?
A: The combination of PoH + PoS + efficient consensus is unique to Solana and gives it advantages in speed and cost.
📚 References and Further Reading
- Solana Documentation - Official technical documentation
- Solana Cookbook - Developer tutorials and examples
🔗 Related Topics
Now that you understand how Solana works, you might want to learn about:
- Transactions and Fees - How much things cost and how to optimize
- Wallet Basics - How to store and use SOL
- Creating Tokens - How to build on Solana
- What is Solana - Understanding Solana’s purpose and benefits
